
In a Windows Active Directory environment, replication is used to ensure that changes made to the directory on one domain controller are propagated to all other domain controllers in the same domain. Replication occurs automatically and periodically between domain controllers, but there are times when you may need to force replication manually.
Here are some reasons why you might need to force replication between domain controllers:
- To ensure that changes made to the directory are propagated immediately: By default, domain controllers replicate changes every 15 minutes (for intersite replication) or every 5 minutes (for intrasite replication). If you make a change to the directory and want it to be replicated immediately, you can force replication manually.
- To troubleshoot replication issues: If you suspect that there is a problem with replication, you can force replication manually to see if it resolves the issue.
- To initialize replication for a new domain controller: When you add a new domain controller to an existing domain, you may need to force replication to ensure that it has a current copy of the directory.
Command to manually force replication
You can force replication between domain controllers with the following command:
repadmin /syncall /AdeP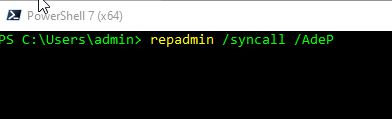
The /AdeP switch in the repadmin /syncall command specifies that replication should occur for all directory partitions, including those that are not held on the local domain controller. The A switch specifies that all directory partitions should be replicated, d specifies that replication should be performed in the same direction as the domain controller is configured to replicate, e specifies that enterprise level replication should be performed (i.e. to all domain controllers in the forest), and P specifies that replication should be pushed to other domain controllers rather than pulled. By including the /AdeP switch, you ensure that all domain controllers have a current copy of the directory.
Default Sync Time for Windows Domain Controllers
The default sync time between domain controllers depends on the version of Windows Server you are using. In Windows Server 2003 and earlier versions, the default sync time was 3 hours for intersite replication and 15 minutes for intrasite replication. In Windows Server 2008 and later versions, the default sync time is 180 minutes for intersite replication and 15 minutes for intrasite replication.
You can adjust the default replication time schedule by following these steps:
- Log in to a domain controller with an account that has administrative privileges.
- Open the “Active Directory Sites and Services” console. You can do this by clicking “Start”, selecting “Administrative Tools”, and then clicking “Active Directory Sites and Services”.
- Expand the “Sites” folder, and then expand the site that contains the domain controller whose replication schedule you want to modify.
- Expand the “Servers” folder, and then click on the domain controller whose replication schedule you want to modify.
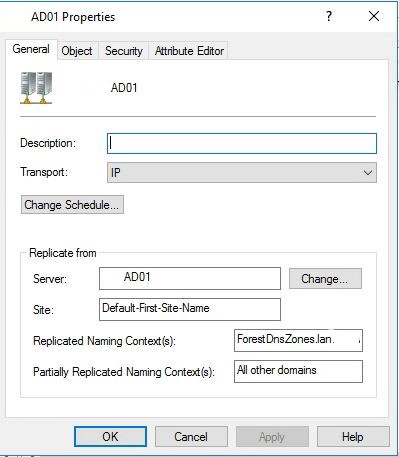
- Right-click on the “NTDS Settings” object for the domain controller, and then select “Properties”.
- In the “NTDS Settings Properties” dialog box, click on the “General” tab.
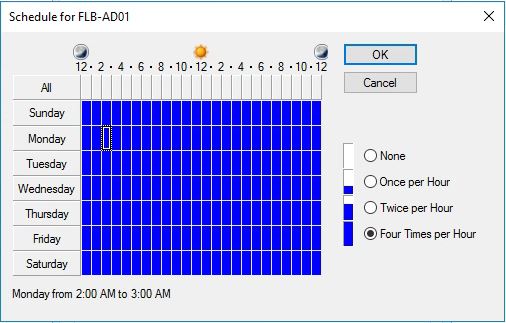
- Under the “Replication Interval” section, you can modify the default replication interval for intrasite and intersite replication. For example, if you want to change the default intrasite replication interval from 15 minutes to 30 minutes, select the “Change” button next to “Intrasite replication interval (minutes)” and set the value to 30.
Note that modifying the replication interval can affect the amount of network traffic generated by replication, so you should use caution when making changes. Also, keep in mind that changing the replication interval for one domain controller does not affect the replication interval for other domain controllers. If you want to modify the replication interval for all domain controllers in a site, you will need to repeat these steps for each domain controller in the site.
